MAC address stands for media access control address. It is also used to communicate or transfer data from one computer to another. This is nothing but a unique 48-bit hardware number of a computer. During manufacturing, it is a technique to represent the word into a network card known as NIC(Network Interface Card). This is also known as the physical Address of the device. It is a unique address that exists in several network devices.
Table of Contents
Definition
A unique identifier allows a network interface controller to use a network address in communications with a network segment. This is commonly used in IEEE802 networking technologies, ethernet Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth.
Format
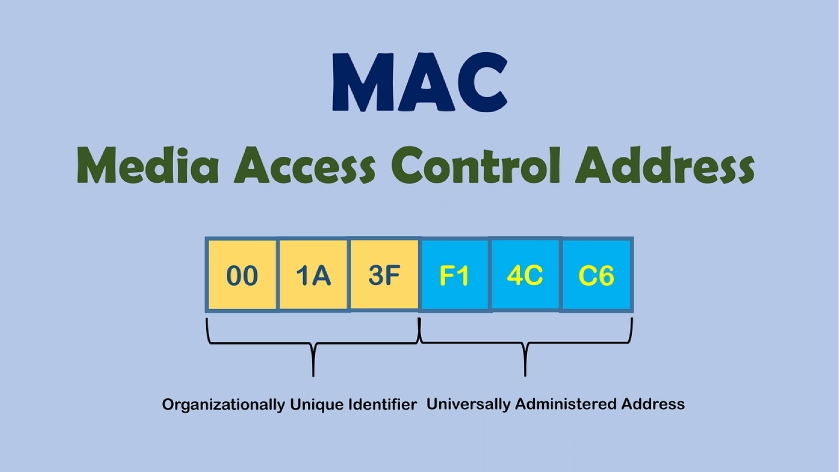
In this, It has 12 digits hexadecimal number containing six bites binary numbers. It is mainly represented by Colon-Hexadecimal notation. The manufacturer identifies the First six digits of the MAC Address. It is also called the OUI (Organizational These Macs are posted by the IEEE Registration Authority Community, which prefixes to its registered vendors.
Here are some OUI creators:
Cisco – CC:46:D6
Google- Inc. 3C:5A: B4
Hewlett Packard-3C: D9:2B
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO-LTD00:9A: CD
Types
Here are some of the types
Unicast MAC address: A unique address represents a unique network. It also means a single address should represent a single address.
Multicast MAC Address: The device that can transmit data to multiple devices using a multicast.
Broadcast MAC address : This represents every device on a given network. Its purpose is to broadcast a domain that enables a device to send the data to every device on the web by using the broadcast address as the destination’s MAC address.
Below are some of the Advantages
- Uniqueness: Each MAC address is unique, by which the device can also be identified and quickly managed by the network.
- Simplicity: They do not require additional network infrastructure as they are easy to configure and manage.
- Compatibility: These are very compatible systems that are very wide and also support different types of protocol and networking technologies.
- Security: These devices are authorized with a Mac address to connect and allow the network when access is restricted.
- Fault-tolerance: A device can be easily replaced without affecting the network if the new device has the same MAC address as the old one. In case of hardware or software failure
- Efficiency: It also allows them to communicate efficiently on the present network, enabling the other devices to communicate quickly and easily.
Here Are Some of The Drawbacks
- Limited address space: This has 48-bit numbers. There is a possibility in the Mac address if the numbers are finite. This also can lead to conflict if the Mac addresses the same in multiple devices.
- Spoofing: It can quickly gain address access to the network and easily spoofed, allowing unauthorized devices
- Inefficiency: It can make it challenging to manage large networks by hierarchy efficiently.
- Static addressing: These are typically assigned during manufacture and cannot be easily changed. It’s a disadvantage when devices need to be reconfigured or replaced.